Encyclopedia of Marketing. What is FMCG? Consumer Goods What is an fmcg company
Every person is familiar with FMCG companies, because we use their products every day, hence the name of the fast moving consumer goods (FMCG) sector - everyday goods. FMCG companies include Unilever, which produces detergents, Johnson & Johnson, which sells medicines and cosmetics, and Sun Interbrew | AB InBev, which produces beer, and Philip Morris International, known for its tobacco products. FMCG is drinks, chocolate, hygiene items and other goods that are needed by customers on an ongoing basis and are characterized by a relatively low price.
FMCG companies face the difficult task of not only retaining a huge number of customers, but also constantly increasing profits by attracting new customers. A successful business in the FMCG sector is determined primarily by the company's ability to effectively innovate and apply non-standard approaches to solving ambitious tasks, and this inevitably depends on the quality and competence of the staff. That is why the leaders of the FMCG market pay special attention to the recruiting process: the employee selection system in FMCG is one of the most stringent and complex.
How to get a job in FMCG?
For many FMCG companies, it is not so much the basic education of potential employees that matters, but their personal qualities and competencies. The ideal candidate for the FMCG sector is an active, dynamic person who can work independently, communicate effectively and think outside the box. FMCG companies are in a constant struggle for the consumer, so they need people who can make decisions with lightning speed, overcome difficulties and achieve results. A prerequisite is the ability to work in a team and good leadership potential.
It is practically impossible to reveal all these qualities and skills during a regular interview. Therefore, the selection process in FMCG companies usually includes several stages: psychological testing, ability testing, and only then an interview. Testing allows you to determine at an early stage whether a given candidate is suitable for the company and how well he can cope with the tasks.
For many applicants, testing is the greatest difficulty. This can be partly explained by the fact that while most people are familiar with the interview format, tests are much less common - mainly in large international corporations. The complexity of the FMCG tests themselves cannot be denied: the questions they contain will make you rack your brains and use your abilities to the maximum, which is exactly what they are designed for. The testing phase is a really serious test, but it is quite possible to pass it if in advance.
Testing in FMCG
Designed to assess you as a person as objectively as possible, including intellectual skills - the ability to think logically and rationally, analyze data, find solutions, as well as personal characteristics - communication style, character type, sociability, etc.
Assessment of intellectual skills is carried out through tests to identify abilities, including, as well as. During the test, you are offered several questions of varying difficulty with multiple choice of answers, from which you will need to choose the correct one in a short time. This test allows you to assess your ability to absorb information quickly and efficiently, the ability to read numerical data and draw reasoned conclusions based on them, and the level of your logical thinking.
The personality test is a list of questions related to work and the work process that you will need to answer based on your character and personality. This test gives a potential employer an opportunity to assess whether you can fit into the team and corporate culture of the company.
Benefits of working in FMCG
As you can see, getting a job in FMCG is very difficult, so is it worth spending time on it? FMCG in Russia is one of the most promising areas for building a successful career. Here are just a few of the benefits of working for an FMCG company:
- FMCG companies are always companies with big names. Procter & Gamble, L'Oreal, PepsiCo, Coca Cola - these names are on everyone's lips, because FMCG retail chains are represented all over the world. These are brands that are present in every home and make our lives easier. Working in FMCG is an opportunity to become part of a big family with a global reputation.
- In FMCG, work is not a daily routine, but a continuous development, as this sector is constantly changing, adapting to new habits and needs of people. In whatever field you find yourself - in the tobacco giants British American Tobacco or Japan Tobacco International, the sweet industry Mars Inc or Nestle - you will never be bored.
- FMCG companies respect their employees as much as they respect their customers. Investing in personnel development is the main principle in the FMCG world, because corporations understand that a successful business rests primarily on professional staff.
- The FMCG sector, like no other, is able to withstand financial crises. People may stop buying stocks, real estate, and cars, but they will never stop buying consumer goods. Working in FMCG, you can be sure of stability and a long-term career.
- In FMCG, it’s not your diploma, increase or work experience that matters, only one thing matters here - your achievements.
Best regards, worldcompanyjob team
In this article, we will look at what FMCG products are and what are the specifics of this area. Surely you have come across the abbreviation FMCG (fmsji) and for good reason. This is an abbreviation for consumer goods and the literal translation (fast moving consumer goods) means fast moving consumer goods. All goods that people buy regularly and very often can be attributed to the FMCG group and this creates very strong competition in the developed and technologically advanced market for this product.
FMCG companies themselves are worthy employers with good wages and low staff turnover. . The market itself is quite stable and promising.
FMCG products
What specific groups of consumer goods belong to FMCG?
- Alcohol;
- Food;
- Tobacco products;
- Household chemicals.
Although there are many more varieties of consumer goods, it should be noted that FMCG products: meat, bread, cigarettes, matches, condoms, turn around much faster than: watches, glasses, phones, etc. This means that the buyer of fast goods forms the habit of buying these goods in a certain place and with a certain cyclicity. Therefore, the technologies for selling FMCG goods are developing very quickly, which is reflected in the assortment, convenience and accessibility for the end customer.
The FMCG product group is characterized by some marketing features:
- Low price tag for goods with low profitability. The low price tag forces a private buyer to purchase goods, almost without hesitation, to make a decision on his own without the advice and help of the seller.
- The turnover is very high, so it is necessary to carefully consider the supply of goods and filling the shelves in the store.
- The cyclicity of purchases is high, since bread, tea, washing powder (goods with a short life cycle) end quickly and force a person to make again and again.
Features of FMCG Marketing
The main task of FMCG marketing is to form a sustainable and conscious need for the consumer, but the consumer, in turn, should give preference to the trade brand that could interest him with its assortment, packaging and price. You, as a consumer, may not understand shampoos, but you will definitely choose a product of a certain brand. The manufacturer took care of this in advance.
FMCG (fast moving consumer goods) are fast moving goods, i.e. those that are carried out on a daily basis. This includes food, household chemicals, tobacco products, etc. Everything that you use regularly and without which you cannot imagine your life - all this is FMCG.
FMCG products are also called consumer goods (consumer goods for short). They can be found in any store, supermarket, gas station. Most often, this includes food products, light industry, which is relatively inexpensive, has a wide demand, and is quickly sold. Such goods do not give their owner uniqueness, do not differ in design features, have the same style. Prominent representatives of this group of products are:- cosmetics;
- goods for shaving, oral care, bathing;
- personal hygiene items;
- detergents;
- light bulbs, batteries, plastic goods, paper;
- glassware and other non-durable goods.
- packaged food products, drinks;
- consumer electronics;
- medications.
In Russia, FMCG is often referred to as "goods of mass, high demand", but this is not an entirely correct interpretation. For this category of products, the main thing is not increased demand (after all, it can increase temporarily, seasonally), but the frequency of purchases. For all FMCG products, the demand is constantly increased, regardless of the season, economic and political situation.

* Calculations use average data for Russia
INTRODUCTION
The FMCG market is one of the most striking indicators of the economic situation in the country. It reflects not only consumer sentiment and confidence, but also the level of solvency, since most FMCG products are essential goods.
According to the definition, FMCG (fast moving consumer goods) are goods of daily consumption by a wide range of buyers that have a relatively low cost and high turnover. In other words, these are consumer goods:
Personal hygiene items
Cosmetics
Products for cleaning teeth and shaving
Detergents
Light bulbs, batteries and other non-durables
Food (sometimes treated as a separate category, but more often as FMCG)
A distinctive feature is the low profitability of this type of goods, however, due to large sales volumes and fast turnover, they represent an economically profitable category.
MARKET ANALYSIS
The market for food and non-food FMCG products has been demonstrating a stable downward trend in turnover since the second half of 2014. The reasons for this are the decline in real incomes of the population, Western sanctions, the depreciation of the national currency and other negative factors.
For the entire period from 2014 to 2016, there was only one burst of activity in the market, when the population actively tried to invest cash as much as possible. However, the real growth rate of retail trade in 2014 was 2.5%, while in 2013 this figure was at the level of 3.9%. The decrease in sales volumes forced the players to reconsider their work models, to significantly change their assortment policy and logistics. With a decrease in turnover in physical terms, in monetary terms, according to RBC, the turnover of retailers increased by 30%. The share of network retail (foodstuffs) in the market structure has also increased; in 2014 it amounted to 37.8% (+5.8 p.p.).
In general, the development of network retail in Russia is uneven. The supply of chain stores per capita lags far behind the indicators of developed countries. At the same time, in some cities there is an excess of chain retailers, while in others there is a lack of them.
According to analysts, by the middle of 2015 a number of trends have formed that will determine the further development of the market until the end of 2017:
Increasing the variety of formats within one retail chain, including through the introduction of discount formats (discounters);
Increasing the share of modern formats in FMCG retail up to 60-65% in 2016;
An increase in the share of Russian-made goods in the assortment (up to 40-50%) and in the revenue of chains associated with the policy of import substitution; development of own production;
The growing popularity of discounters (stores with an assortment of low price segment);
Decreased consumer activity of the population, reduced costs, high degree of price influence on the purchase decision;
Changing the development strategy and business models of networks to reduce the share of borrowed funds in total capital due to their high cost;
Refusal to open some new stores (however, some discount chains, on the contrary, began to actively master the format of “convenience stores”;
Growing influence of state regulation of the industry, increasing the tax burden on business.
The dynamics of GDP growth reflects the general state of the entire economic system of the country. If at the end of 2011 - beginning of 2012 GDP showed growth of 4-5% per quarter, then in the II quarter of 2015, with a stable preliminary fall, it was already -5%. However, at the beginning of 2016, the drop dropped to -1%.
The prerequisites for the crisis are obvious: EU and US sanctions, the weakening of the ruble, a significant drop in oil prices. As a result of these processes, the cost of imported products has increased significantly. Since the production of many domestic goods uses imported technologies, raw materials, components, equipment, and so on, prices for products of Russian manufacturers have also increased. According to Rosstat, prices for goods and services in 2015 increased by an average of 12.9% compared to 2014.
Earn up to
200 000 rub. a month, having fun!
2020 trend. Intelligent entertainment business. Minimum investment. No additional deductions or payments. Turnkey training.
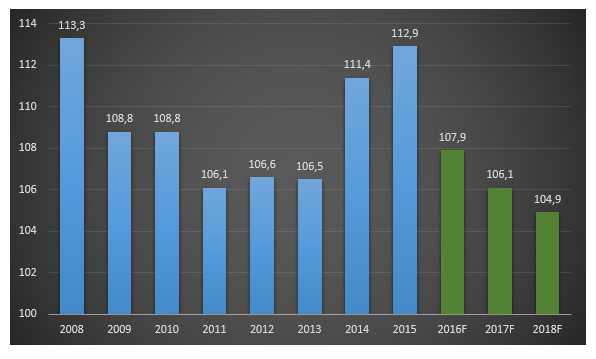
Figure 2. Consumer confidence index, 2008 Q1 – 2016 Q1

As can be seen from Fig. 2, the index of consumer confidence of the population approached the values of the crisis year of 2008, which directly affects the development of retail trade. Nevertheless, experts, in particular RBC.Quote, predict an improvement in the economic situation in 2017-2018. and the growth of quotations for Brent oil to $66.4 per barrel. Experts also predict a slowdown in inflation and growth in consumer prices (up to 4.9%).
Nevertheless, even against this backdrop, according to the forecasts of the Ministry of Economic Development, the real disposable income of Russians in 2016 will decrease by 2.8% due to high debt load, rising prices, unstable economic and political situation and other factors. This will force the population to take a more balanced approach to spending.
Figure 3. Nominal volume of retail trade in the Russian Federation, billion rubles, 2009-2018 (RBC data, according to the sources of the Ministry of Economic Development, the Ministry of Industry and Trade)

In the long term until 2018, experts predict an increase in household incomes, a restoration of the consumer lending system, which will lead to an increase in consumption. In 2018, according to forecasts, the growth of retail trade turnover will be 3.7% in real terms. The savings rate will decrease, which will lead to some increase in spending by the population.
Ready-made ideas for your business
Retail trade and the service market have traditionally supported the growth of Russian GDP. However, against the background of the economic downturn, these segments began to lose their role as the main factors in the development of the economy.
Figure 4. The share of retail trade in the structure of Russia's GDP, %, 2004-2014

Figure 5. Share of retail trade turnover of retail chains in total retail trade turnover, %

In the non-retail retail segment, there is a decrease in the number of small and micro enterprises associated with increased competition from retail chains, as well as an increase in the tax burden on small businesses and an increase in the cost of loans.
Ready-made ideas for your business
There have been no significant changes in the structure of retail formats in recent years. The discounter format showed some growth, while the supermarket format showed a decrease, which will continue to decline in the short term. Large-format retail (hypermarkets) showed high resistance to crisis factors, but its share still slightly decreased. Growth was shown by convenience stores. This format is currently being developed by both federal companies and, traditionally, by local players.
Since 2013, experts have noted a significant increase in the share of “other” formats: eco-goods stores, “fix-price” format stores, etc. In 2014, they accounted for at least 10% of the total retail trade turnover. Presumably, this share will grow.
The number of own chain stores of food manufacturers is also growing: poultry, dairy products, bakery products.
Figure 6. Structure of retail formats (by number of outlets) in Russia
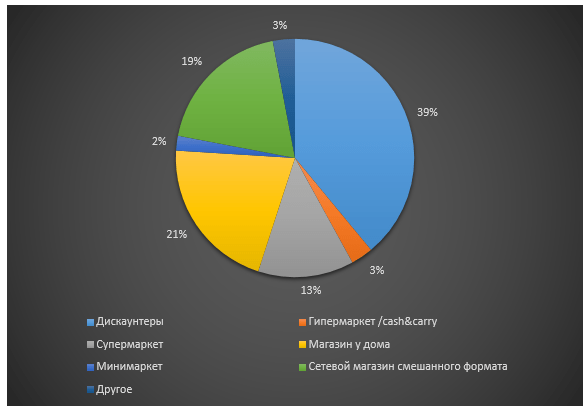
Retail market development forecasts (FMCG segment):
Reducing the share of large-format retail and increasing the share of discounters (within 35%)
Reducing the share of supermarkets against the backdrop of a decrease in customer traffic
Development of convenience stores (up to 12-13% in total)
Emergence of new store formats
Denis Miroshnichenko
(c) - portal of business plans and guides for starting a small business
1759 people are studying this business today.
For 30 days this business was interested in 50563 times.
Profitability calculator for this business

The textile industry in Russia is in a state of decline due to the low level of product competitiveness. In general, even with the successful process of reorganization of the industry, it is hardly worth a...
FMCG - what is it? The article provides an answer to this question, and also tells how this system works, what goods belong to this group, and why this particular segment has a high demand and turnover. It also presents the tools that companies need to always be afloat and keep a good competitive defense.
FMCG - what is it?
Probably, many at least once in their lives have come across such a concept. It means consumer goods with fast turnover. This includes categories of goods that are purchased by people constantly.
FMCG companies are ranked as worthy employers with high wages and low staff turnover. In addition, they are highly competitive.
The segment of goods in this category is divided into purchases with a margin, for the arrival of guests and everyday purchases. To maintain their position, companies have to constantly improve their product and conduct promotions. Successful manufacturers have a wide range, and their brand is always heard.
Kinds
The FMCG segment is characterized by fast sales and low prices. The consumer demand for them is high due to the fact that they serve for a certain period of time. After that, the purchase will need to be made again. Of course, the bulk proceeds from such sales are small amounts. However, the profit is very significant due to the fast and large turnover.

Depending on the type of destination, goods are for everyday use and for stock.
- Shampoos, shower gels, toothpaste and other hygiene items.
- Powders, cleaning products and more.
- Tobacco and alcoholic products.
- Carbonated drinks.
- Cosmetical tools.
- Medications.
- Batteries and light bulbs.
It should be noted that sales of this category of goods are less dependent on the crisis periods of the economy. While large household appliances, electrical appliances usually change about once every 2 years, if not less often.
How does it work
We have already found out that the goods of this segment have a fast turnover. Consider the marketing components:
- Low price for goods with low margins.
- When selling this segment, you do not need additional advertising and the help of a consultant. The buyer purchases the goods, not particularly thinking about its cost and necessity at the moment.
- High demand is accompanied by strict control over the filling of empty shelves.
- Repeat purchases are made again! Goods such as toothpaste, washing powder, shampoos and others run out quickly.

In hypermarkets, supermarkets and small shops, such a product segment is mainly placed at the checkout, butts and promo zones. The more people see the product, the more likely it is to sell. Merchandisers and sales representatives of their brand have well-designed instructions on what and where should be located.
Basic FMCG tools
The more stores and retail outlets a manufacturer covers, the better sales will affect its revenue and turnover. You have probably noticed that famous brands are found almost anywhere.

The best artists worked on the packaging design of this product. Everything in it should attract the eye of the buyer: font size, colors and pictures. Often, in order to earn the client's trust in his trademark, a representative uses such inscriptions: light bulb - savings, candy - based on natural juice, toothpaste - natural ingredients.
The best-selling products are located at the level of the human eye. This technique is well thought out. There are shelves in the store, passing by which we stop looking at the product of interest. They are located at a distance of 150-170 centimeters from the floor. Less priority products are placed on the lower and higher shelves.
The product is analyzed by analysts in retail outlets and centers, sales reports are generated for each brand and product for the required period.
Sales Secrets
There is no single methodology that would ideally work for the entire FMCG sector. Consider the main professional tools:
- Location of goods on the promotional shelves.
- Teamwork with all project participants (manufacturing company - supplier - advertising - personnel involved in promotions).
- Advertising should not be only on TV. Periodic consultations in large shopping centers, on the Internet, and so on, are simply necessary for a qualitative increase in sales.
- Digital - advertising.
- Finding a stronger incentive to buy your brand.
- Analysis of the effectiveness of the advertising campaign.

It is enough to consider the work of the FMCG network using the example of Magnit, Lenta, Auchan and others. Their profits are only growing, the number of stores is increasing, and the turnover is increasing every year.
Basic rules in the operation of the FMCG market
FMCG - what is it and what are the foundations for the successful existence of the strategy? The segment is characterized by healthy competition and the frequent emergence of new companies engaged in the production of goods in a similar category. To maintain a leading position in the market, companies need to constantly expand and improve their product, maintain optimal price levels by optimizing costs, and at the same time remember to regularly advertise their brand.
The correct positioning of the product on the shelves plays a fundamental role in increasing sales. The client's trust in the brand must always be warmed up, only in this way it is possible to achieve an increase in turnover.
So we have sorted out the question of FMCG - what is it and what are the foundations for the successful existence of the strategy. The easiest way in this market is for companies whose brand belongs to monopolists, such as Coca-Cola. It should be noted that the wider the range, the higher the turnover. Although this brand has enough trust from the client, which is also important. Dairy products producers have a more precarious position, as there are about 2-3 main items in the assortment (cottage cheese, kefir, yogurt), and competition is high.
Multi-products that cover a wide segment of the market and continue to grow at an active pace. This applies to manufacturers such as P&G, Nestle, etc.
